Topic icd-10 code for moisture-associated skin damage buttocks: Discover the essential ICD-10 codes for moisture-associated skin damage on buttocks, unlocking vital insights for effective diagnosis, treatment, and management strategies to enhance patient care and outcomes.
Table of Content
- Understanding MASD
- New ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes
- Impact of New Codes
- What is the specific ICD-10 code for moisture-associated skin damage on the buttocks?
- Introduction to Moisture-Associated Skin Damage (MASD)
- YOUTUBE: Deep Tissue Injury Management
- New ICD-10-CM Codes for MASD
- Understanding MASD and Its Impact
- Preventive Measures and Management of MASD
- The Importance of Accurate Diagnosis and Coding
- Impact of New Codes on Patient Care and Research
- Education and Awareness for Healthcare Providers
- Future Directions in MASD Treatment and Research
Understanding MASD
MASD occurs from prolonged skin exposure to moisture or irritants, causing inflammation or erosion. This condition can feel similar to sunburn and may escalate to more severe skin issues if not managed properly. However, with proper attention, MASD is both preventable and manageable.

READ MORE:
New ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes
The introduction of specific codes for MASD allows for better tracking, research, and treatment of this condition. Below are the new codes:
- L24A0 - Irritant contact dermatitis due to friction or contact with body fluids, unspecified
- L24A1 - Irritant contact dermatitis due to saliva
- L24A2 - Irritant contact dermatitis due to fecal, urinary or dual incontinence
- L24A9 - Irritant contact dermatitis due to friction or contact with other specified body fluids
- L24B0 - Irritant contact dermatitis related to unspecified stoma or fistula
- L24B1 - Irritant contact dermatitis related to digestive stoma or fistula
- L24B2 - Irritant contact dermatitis related to respiratory stoma or fistula
- L24B3 - Irritant contact dermatitis related to fecal or urinary stoma or fistula
Impact of New Codes
The new codes facilitate enhanced data capture, research, and education on MASD. They support the health care system in accurately documenting and treating the condition, improving patient outcomes. This advance also enables the analysis of large data sets for better clinical and research insights into MASD management and treatment effectiveness.
For More Information
Healthcare professionals are encouraged to familiarize themselves with these new codes to improve MASD diagnosis and treatment. The initiative represents a significant step forward in the documentation and management of skin conditions associated with moisture exposure.

What is the specific ICD-10 code for moisture-associated skin damage on the buttocks?
The specific ICD-10 code for moisture-associated skin damage on the buttocks is L22.23.
Introduction to Moisture-Associated Skin Damage (MASD)
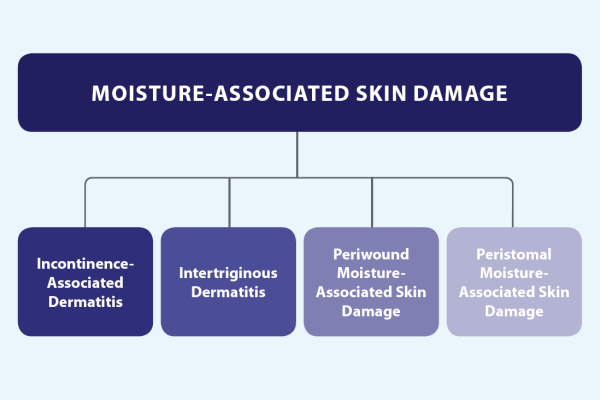
Moisture-Associated Skin Damage (MASD) represents a significant concern in healthcare, characterized by inflammation and erosion of the skin due to prolonged exposure to various sources of moisture. These sources include bodily secretions such as urine, fecal matter, perspiration, wound exudate, mucus, digestive and respiratory secretions, or saliva. MASD encompasses several conditions, including incontinence-associated dermatitis, intertriginous dermatitis, periwound skin damage, and peristomal skin damage, each with unique challenges in prevention and management.
This condition not only affects patient comfort and quality of life but also poses a risk for further complications, such as infection or delayed wound healing. Understanding MASD is crucial for healthcare professionals to implement effective prevention strategies, timely diagnosis, and appropriate management plans tailored to individual patient needs.
- Incontinence-associated dermatitis (IAD) is primarily observed in patients with urinary and fecal incontinence, leading to skin damage in perineal and genital areas.
- Intertriginous dermatitis (ITD) occurs in skin folds due to the combination of moisture, friction, and lack of air circulation.
- Periwound skin damage affects the skin surrounding chronic wounds, exacerbated by exudate from the wound itself.
- Peristomal skin damage arises around ostomy sites, where effluent from the stoma irritates the skin.
Effective management of MASD involves a comprehensive approach that includes assessment, cleansing, moisturizing, protecting the skin, and educating patients and caregivers. By addressing the root causes of moisture and implementing barrier protections, healthcare providers can significantly reduce the incidence and severity of MASD, thereby improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Deep Tissue Injury Management
Learn valuable strategies and techniques in this video on effective management practices. Enhance your skills in leadership, organization, and problem-solving, empowering yourself to excel in both your professional and personal life.
New ICD-10-CM Codes for MASD
The introduction of new ICD-10-CM codes for Moisture-Associated Skin Damage (MASD) marks a significant advancement in healthcare documentation and patient care. These codes, spearheaded by the Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Nurses Society (WOCN), have been officially approved and implemented to provide a more detailed and accurate way to document MASD conditions. With these codes, healthcare providers can better identify, treat, and manage MASD, ultimately improving patient outcomes and facilitating more precise research and analysis in this area.
- The new codes allow for the specific classification of various MASD conditions, enabling healthcare professionals to accurately document the type and severity of skin damage.
- By improving the specificity of diagnoses, these codes enhance the quality of patient care through tailored treatment plans and management strategies.
- They also play a crucial role in research by allowing for the collection of more detailed data on the prevalence and outcomes of MASD, thereby informing future best practices and treatment modalities.
- The adoption of these codes reflects a broader commitment within the healthcare community to recognize and address the complexities of skin health, particularly in vulnerable populations.
Overall, the new ICD-10-CM codes for MASD represent a pivotal step forward in the comprehensive management of skin integrity, underscoring the importance of accurate documentation and evidence-based care strategies in improving patient health and well-being.

Understanding MASD and Its Impact
Moisture-Associated Skin Damage (MASD) significantly impacts patient health, wellbeing, and healthcare systems worldwide. MASD, a result of prolonged exposure to moisture, such as bodily secretions, leads to skin breakdown, irritation, and potential infection. Understanding its implications is crucial for effective prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
- MASD can lead to severe discomfort and pain, affecting patients" quality of life and mobility.
- It increases the risk of secondary infections, including bacterial and fungal skin infections, further complicating patient care.
- Managing MASD requires multidisciplinary approaches, including nursing, dermatology, and wound care expertise.
- Prevention strategies are key in reducing the prevalence of MASD, involving patient education, skin care protocols, and the use of moisture barriers.
- The economic impact of MASD on healthcare systems is significant, with increased costs associated with extended hospital stays, additional treatments, and increased care needs.
Effective management and prevention of MASD not only improve patient outcomes but also reduce the burden on healthcare systems. It highlights the importance of ongoing education, research, and policy development to address this pervasive issue.
Preventive Measures and Management of MASD
Preventing and managing Moisture-Associated Skin Damage (MASD) involves a comprehensive approach that focuses on maintaining skin integrity, patient education, and the use of specialized care protocols. Effective strategies are crucial for enhancing patient comfort, preventing complications, and promoting healing.
- Regular Skin Assessments: Conducting regular and thorough skin assessments helps in early identification of MASD, enabling timely intervention.
- Moisture Management: Use absorbent products and skin barriers to protect the skin from excessive moisture. Changing incontinence products frequently and ensuring dry skin can prevent MASD.
- Skincare Regimen: Implement a gentle skincare regimen using pH-balanced cleansers and moisturizers to maintain skin health and resilience against moisture damage.
- Education and Training: Educate patients, families, and caregivers about the importance of skin care, signs of MASD, and preventive measures to reduce risks.
- Nutritional Support: Adequate nutrition and hydration play a vital role in skin health and recovery. Providing nutritional assessments and support can enhance skin integrity and aid in MASD prevention.
- Interdisciplinary Approach: Collaboration among healthcare professionals including nurses, physicians, dietitians, and physical therapists ensures a holistic approach to MASD prevention and management.
By integrating these strategies into patient care plans, healthcare providers can significantly mitigate the risks associated with MASD, improve patient outcomes, and enhance the quality of life for those affected by this condition.

The Importance of Accurate Diagnosis and Coding
Accurate diagnosis and coding of Moisture-Associated Skin Damage (MASD) are paramount for effective patient care and healthcare management. The recent introduction of specific ICD-10-CM codes for MASD represents a significant step forward in acknowledging the complexity and diversity of skin conditions associated with moisture. These advancements facilitate precise documentation, enable targeted treatment strategies, and improve patient outcomes.
- Enhanced Patient Care: Precise coding allows for tailored treatment plans, addressing the specific needs and conditions of each patient, thereby improving the quality of care and patient satisfaction.
- Improved Documentation: Accurate documentation of MASD through specific codes helps in tracking and monitoring the incidence and outcomes of these conditions, contributing to better patient management.
- Focused Research and Education: With standardized diagnosis codes, research on MASD can be more focused and yield more meaningful insights, leading to advancements in treatment and preventive measures. It also aids in the education of healthcare professionals about the nuances of MASD.
- Healthcare Policy and Reimbursement: Proper coding ensures that healthcare facilities are appropriately reimbursed for the care provided to patients with MASD, supporting the financial sustainability of these essential services.
The integration of these new ICD-10-CM codes into healthcare practices highlights the importance of accurate diagnosis and coding in enhancing patient care, supporting clinical research, and ensuring the effective use of healthcare resources.
Impact of New Codes on Patient Care and Research
The recent approval and implementation of new ICD-10-CM codes for Moisture-Associated Skin Damage (MASD) have had a transformative impact on both patient care and clinical research. These changes facilitate a more nuanced understanding and treatment of MASD, thereby enhancing patient outcomes and advancing medical knowledge in this critical area of healthcare.
- Improved Patient Outcomes: With the introduction of specific codes for different types of MASD, healthcare providers can now offer more targeted and effective treatment plans, leading to better patient outcomes and faster recovery times.
- Enhanced Clinical Documentation: These new codes enable more accurate and detailed clinical documentation, improving the quality of patient records and enabling healthcare providers to track the effectiveness of treatment protocols over time.
- Increased Research Opportunities: The specificity provided by these codes opens up new avenues for research, allowing for more precise studies on the prevalence, risk factors, and treatment outcomes for MASD. This can lead to the development of more effective prevention and management strategies.
- Better Healthcare Planning and Policy Development: Detailed data derived from these codes can inform healthcare policy and planning, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently to address the needs of patients with MASD.
- Enhanced Reimbursement Processes: The specificity of the new ICD-10-CM codes for MASD also means that healthcare providers can more accurately bill for the care provided to patients with MASD, ensuring appropriate reimbursement and supporting the financial sustainability of healthcare services.
The introduction of these new codes represents a significant step forward in the care and understanding of MASD, underscoring the importance of accurate diagnosis and coding in improving patient care and advancing medical research.

Education and Awareness for Healthcare Providers
Educating healthcare providers about Moisture-Associated Skin Damage (MASD) and the new ICD-10-CM codes is essential for enhancing patient care. Increased awareness and knowledge can significantly impact the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of MASD, ensuring better patient outcomes and more efficient healthcare delivery.
- Comprehensive Training: Healthcare providers should receive comprehensive training on the identification, prevention, and management of MASD, including the use of the new ICD-10-CM codes for accurate documentation and coding.
- Best Practice Guidelines: Adoption of best practice guidelines for MASD care can improve patient outcomes. Providers should be aware of the latest research and recommendations in the field.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Encouraging collaboration among various healthcare disciplines, including nursing, dermatology, and wound care specialists, can foster a holistic approach to managing MASD.
- Utilization of Resources: Healthcare providers should be directed to resources and tools that can assist in the proper assessment and documentation of MASD, including detailed descriptions of the new ICD-10-CM codes.
- Patient Education: Providers play a crucial role in educating patients and caregivers about MASD prevention and management, emphasizing the importance of skin care and early intervention.
By focusing on education and awareness, healthcare providers can ensure that they are fully equipped to address MASD effectively, utilizing the new ICD-10-CM codes to enhance patient care and contribute to the body of knowledge on MASD.
READ MORE:
Future Directions in MASD Treatment and Research
The landscape of Moisture-Associated Skin Damage (MASD) treatment and research is evolving, with new directions promising better patient outcomes and deeper understanding of this condition. The adoption of specific ICD-10-CM codes for MASD represents a significant milestone, paving the way for advancements in both clinical practice and research.
- Personalized Treatment Approaches: Future treatment strategies will likely emphasize personalized care, tailoring interventions to the specific needs and conditions of individual patients, based on the precise classification provided by the new codes.
- Advanced Technology Integration: The use of technology, including telemedicine and digital health records, will enhance the management of MASD by improving access to care and enabling precise monitoring of treatment efficacy.
- Enhanced Preventive Measures: Ongoing research into the causes and risk factors of MASD will inform more effective preventive strategies, reducing the incidence of MASD among at-risk populations.
- Interdisciplinary Research Collaborations: Collaborative research efforts across disciplines such as dermatology, nursing, and wound care will foster a holistic understanding of MASD, leading to innovative treatment modalities.
- Greater Focus on Education and Awareness: Education initiatives targeting healthcare providers, patients, and caregivers will remain crucial in preventing MASD, emphasizing the importance of early detection and intervention.
The future of MASD treatment and research holds promise for significant improvements in patient care, driven by enhanced diagnostic precision, innovative treatment strategies, and a deeper understanding of the condition"s underlying mechanisms.
Embracing the new ICD-10 codes for MASD on buttocks heralds a brighter future in healthcare, ensuring enhanced patient care, precise research, and the promise of innovative treatments for those affected by this challenging condition.





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/082222-loreal-paris-skincare-revitalift-anti-aging-face-moisturizer-embed-33ec8a8263694953a516ca81332f2ec7.jpg)






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Why-your-moisturizer-isnt-working_final-564c059accb84ca988aa5a5fe82d44c6.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(2999x0:3001x2)/Best-Moisturizers-for-Acne-Prone-Skin-PEO-social-e15aab304fff476ea34bb0b3bc591210.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/peo-best-concealers-mature-skin-tout-562b727a81a14bc8a87df4d163d0b3cc.jpg)

